Key Advantages
Cryogenic Optical Solutions Designed for Extreme Environments
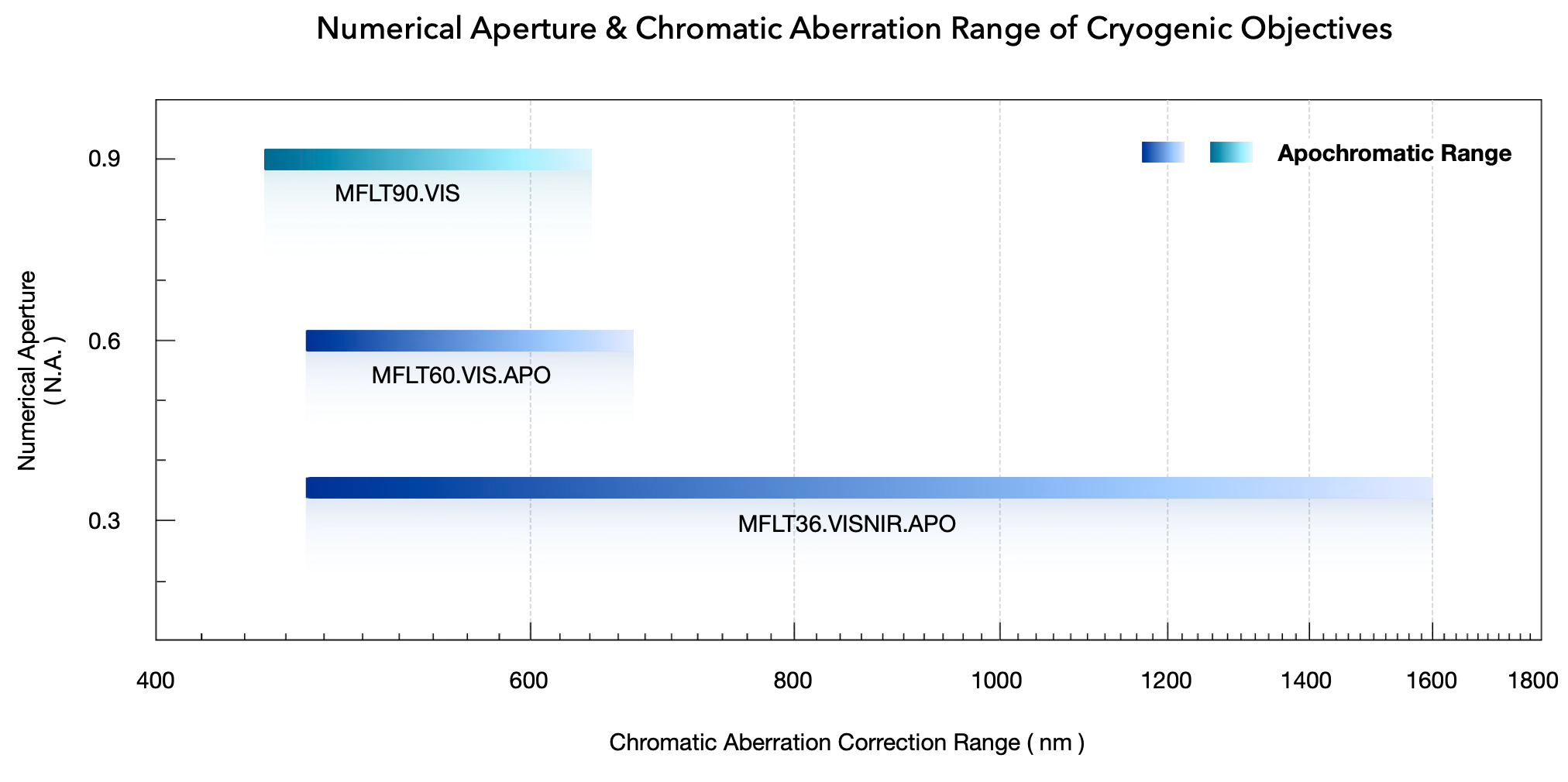
N.A. 0.60
N.A. 0.36
N.A. 0.90
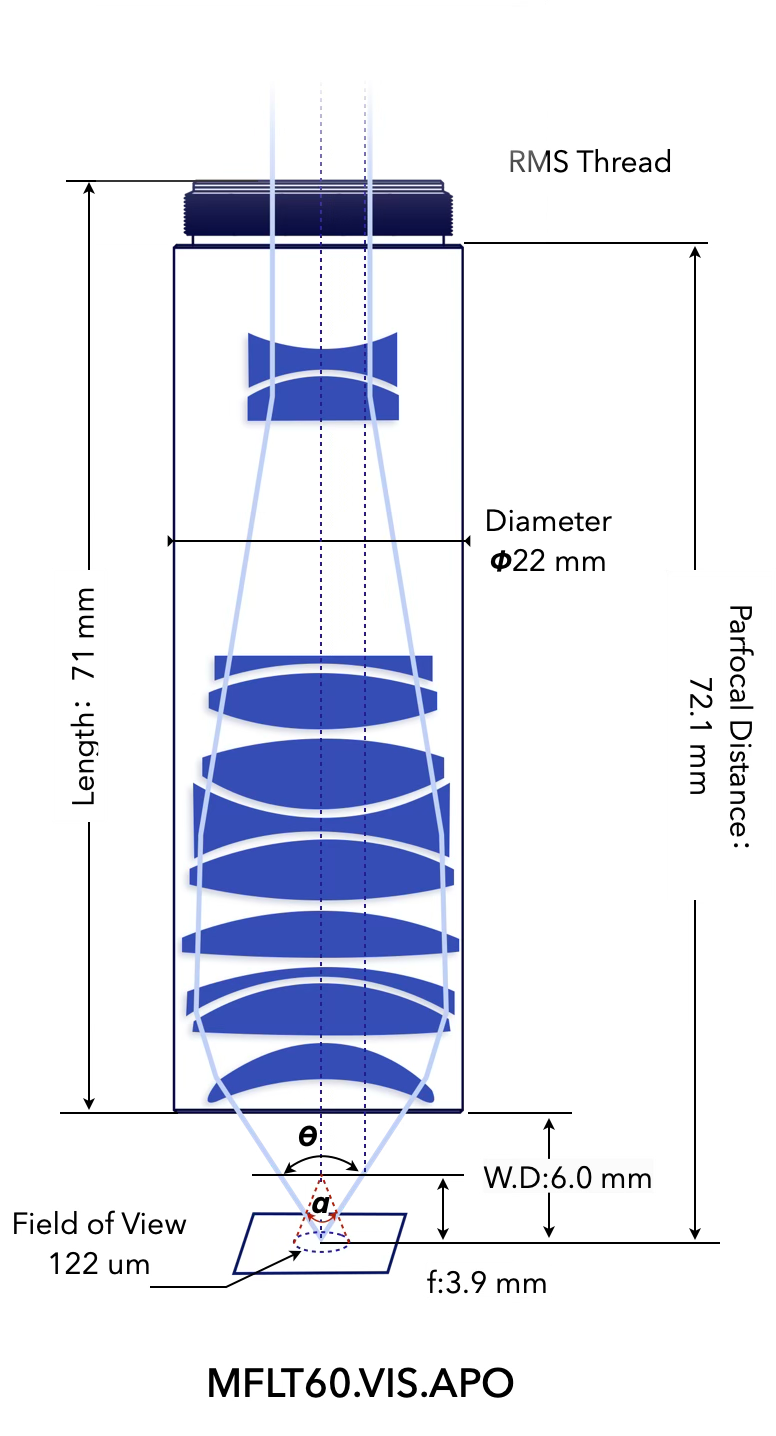
MFLT60.VIS.APO
Ultra-Wide Field of View, Extra-Long Working Distance & Broadband Apochromatic Correction
Specifications
0.6
Numerical Aperture 1 , N.A.
∅ 122 μm
Field of View 2, FOV
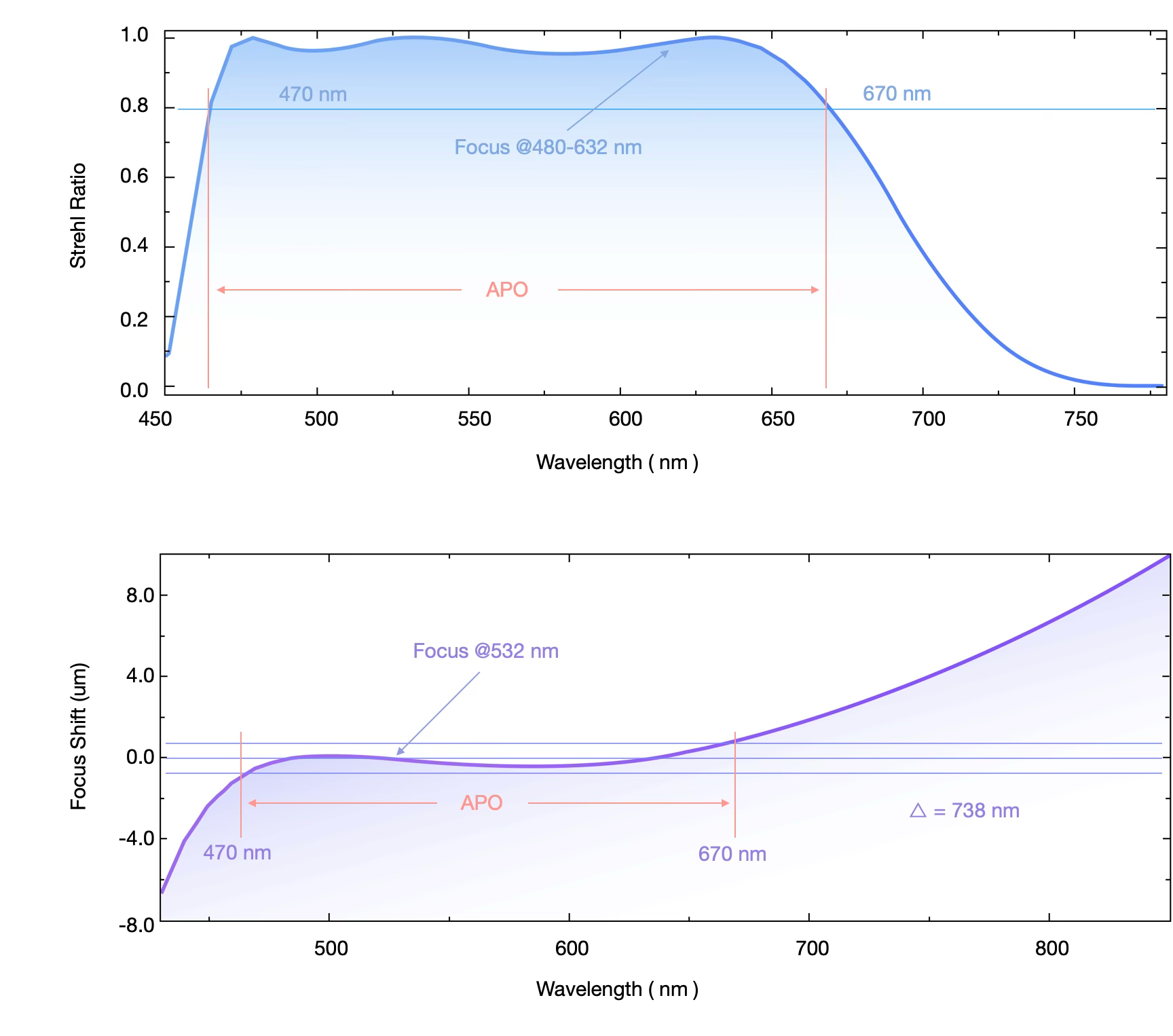
470 – 670 nm
Apochromatic Range 3
430 – 1050 nm @ T > 80%
Anti-Reflective 4, A.R.
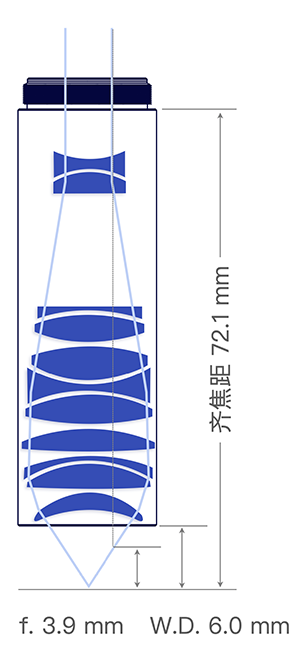
6.0 mm
Working Distance, W.D.
3.9 mm
Focal Length 5, f
Notes
1.Numerical Aperture (N.A.): defines the light-gathering ability and resolution of an objective. It is given by N.A. = n · sin(θ/2), where n is the refractive index of the medium between the objective and the sample, and θ is the maximum acceptance angle of the light cone. A larger N.A. provides higher imaging resolution, with the minimum resolvable distance d = 0.61 λ / N.A., where λ is the light wavelength.
2.Field of View (FOV): Diameter of the area on the focal plane with diffraction-limited imaging.
3.Apochromatic Range: The range of wavelengths over which the focal shift (|df|) of light through the objective remains within the depth of focus (Δ = λ / 2 × N.A.²), ensuring imaging quality is unaffected. Wavelengths satisfying |df| < Δ are considered within the apochromatic range.
4.Anti-Reflective (A.R.): The percentage of transmitted light (T) at specific wavelengths after passing through the objective, relative to the incident light.
5.Focal Length (f): A key optical parameter, defined as the distance from the optical center to the focal point. It is widely used in calculating various optical specifications
-
- Optical Center: The point in the objective where light passes without deviation, serving as the “coordinate origin” of the objective.
- Focal Point: The point where parallel light rays converge after passing through the objective.
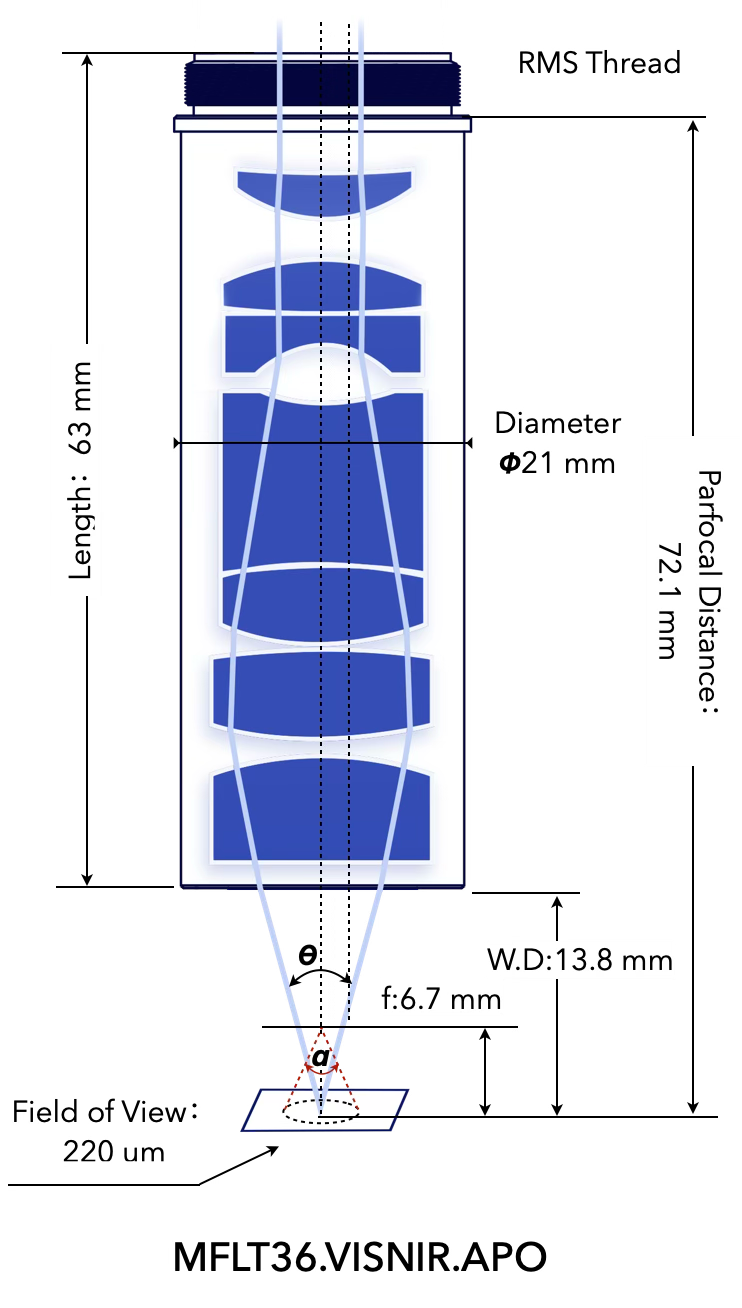
MFLT36.VISNIR.APO
宽波段复消色差,超长工作距离 & 大视野
Specifications
0.36
Numerical Aperture 1 , N.A.
∅ 220 μm
Field of View 2, FOV
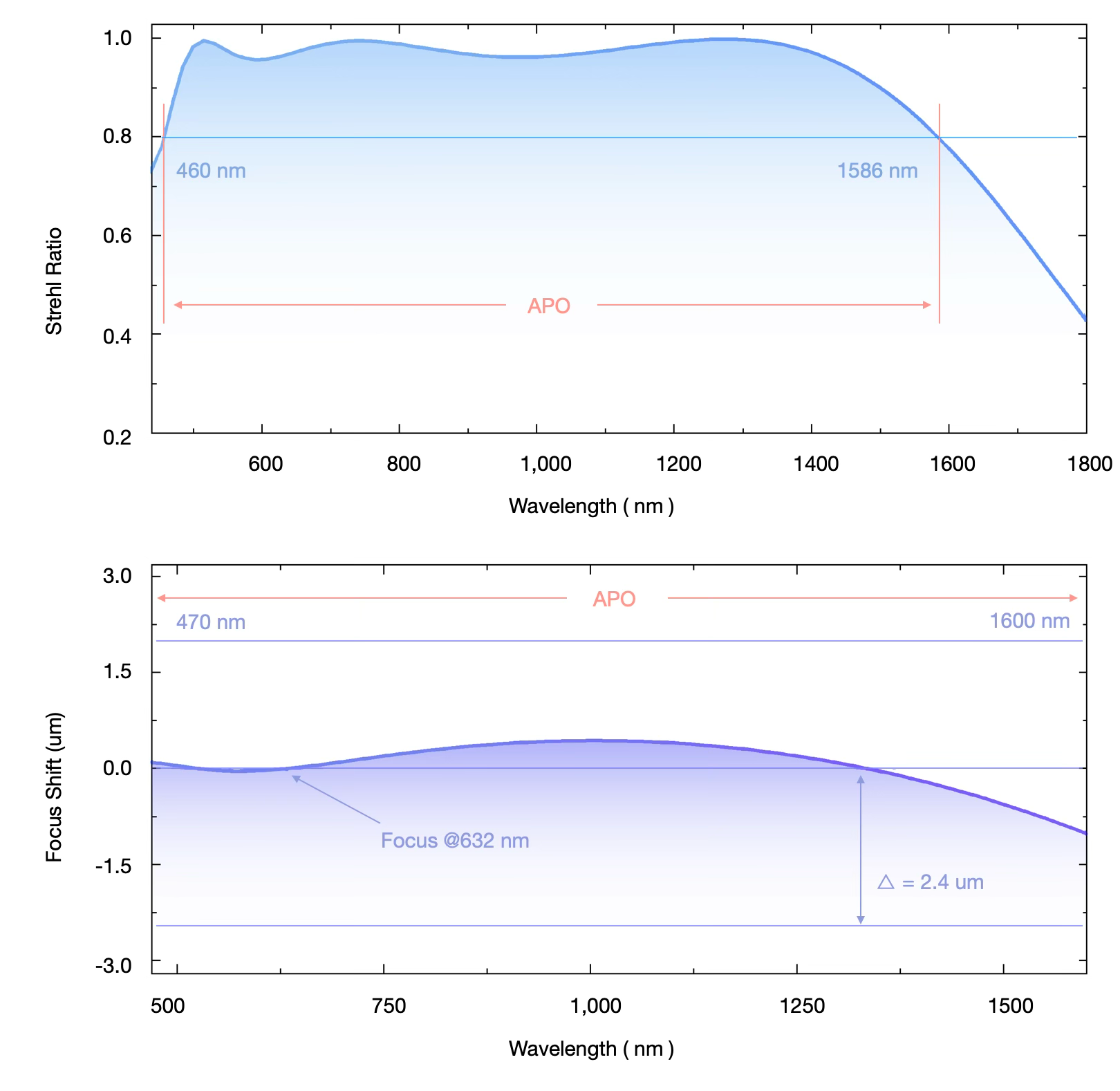
470 – 1600 nm
Apochromatic Range 3
490 – 1500 nm @ T > 80%
Anti-Reflective 4, A.R.
13.8 mm
Working Distance, W.D.
6.7 mm
Focal Length 5, f
Notes
1.Numerical Aperture (N.A.): defines the light-gathering ability and resolution of an objective. It is given by N.A. = n · sin(θ/2), where n is the refractive index of the medium between the objective and the sample, and θ is the maximum acceptance angle of the light cone. A larger N.A. provides higher imaging resolution, with the minimum resolvable distance d = 0.61 λ / N.A., where λ is the light wavelength.
2.Field of View (FOV): Diameter of the area on the focal plane with diffraction-limited imaging.
3.Apochromatic Range: The range of wavelengths over which the focal shift (|df|) of light through the objective remains within the depth of focus (Δ = λ / 2 × N.A.²), ensuring imaging quality is unaffected. Wavelengths satisfying |df| < Δ are considered within the apochromatic range.
4.Anti-Reflective (A.R.): The percentage of transmitted light (T) at specific wavelengths after passing through the objective, relative to the incident light.
5.Focal Length (f): A key optical parameter, defined as the distance from the optical center to the focal point. It is widely used in calculating various optical specifications
-
- Optical Center: The point in the objective where light passes without deviation, serving as the “coordinate origin” of the objective.
- Focal Point: The point where parallel light rays converge after passing through the objective.
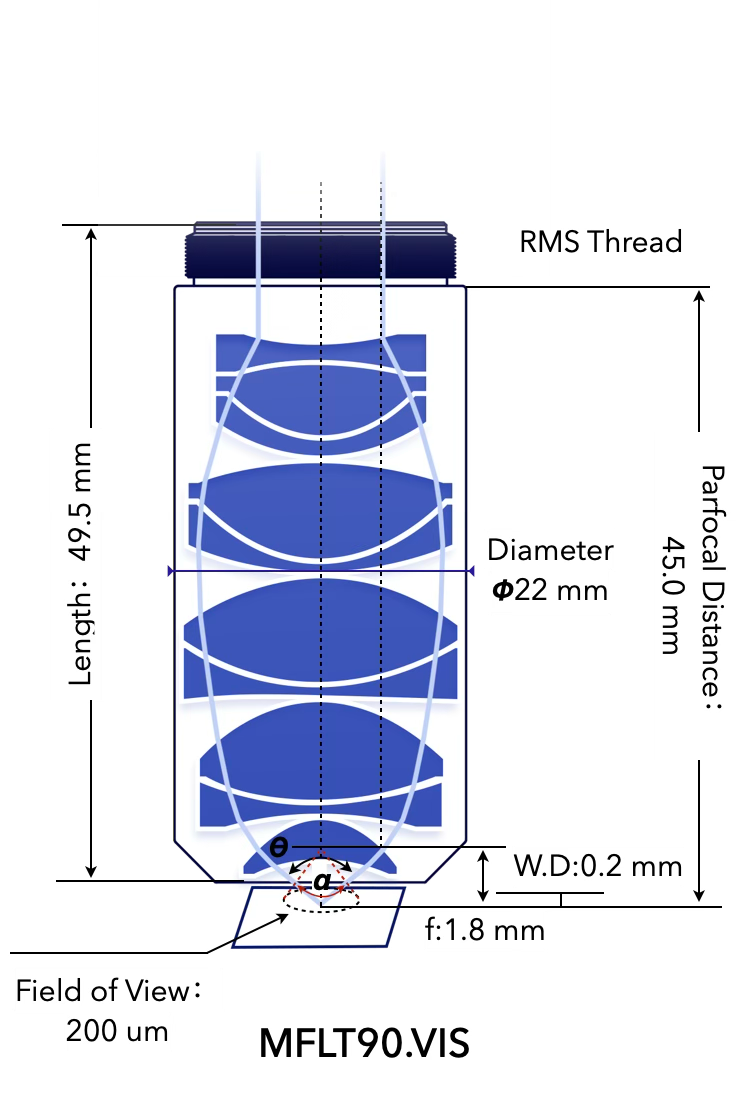
MFLT90.VIS
高数值孔径,大视野 & 紧凑外形设计
Specifications
0.9
Numerical Aperture 1 , N.A.
∅ 220 μm
Field of View 2, FOV
450 – 630 nm
消色差范围3
400 – 750 nm @ T > 80%
Anti-Reflective 4, A.R.
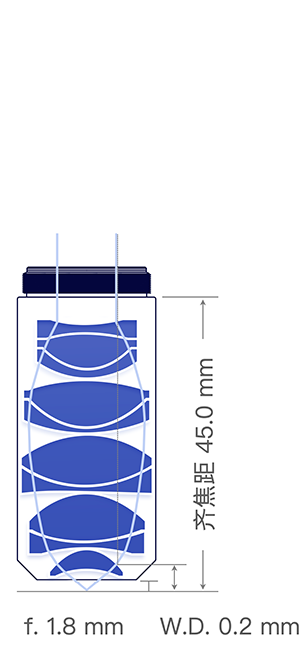
0.2 mm
Working Distance, W.D.
1.8 mm
Working Distance, W.D.
Notes
1.Numerical Aperture (N.A.): defines the light-gathering ability and resolution of an objective. It is given by N.A. = n · sin(θ/2), where n is the refractive index of the medium between the objective and the sample, and θ is the maximum acceptance angle of the light cone. A larger N.A. provides higher imaging resolution, with the minimum resolvable distance d = 0.61 λ / N.A., where λ is the light wavelength.
2.Field of View (FOV): Diameter of the area on the focal plane with diffraction-limited imaging.
3. 消色差范围: 不同波长的光经过物镜后焦点会有变化 ( |df| ), 但只要该变化在焦深 ( △ = λ/2 × N.A.2 ) 范围
内, 则不影响成像质量。df λ1-λ2 < | △ |对应的波长范围 ( 其中λ1和λ2是工作波段的两端 ),称为消色差范围;
4.Anti-Reflective (A.R.): The percentage of transmitted light (T) at specific wavelengths after passing through the objective, relative to the incident light.
5.Focal Length (f): A key optical parameter, defined as the distance from the optical center to the focal point. It is widely used in calculating various optical specifications
-
- Optical Center: The point in the objective where light passes without deviation, serving as the “coordinate origin” of the objective.
- Focal Point: The point where parallel light rays converge after passing through the objective.
Applications
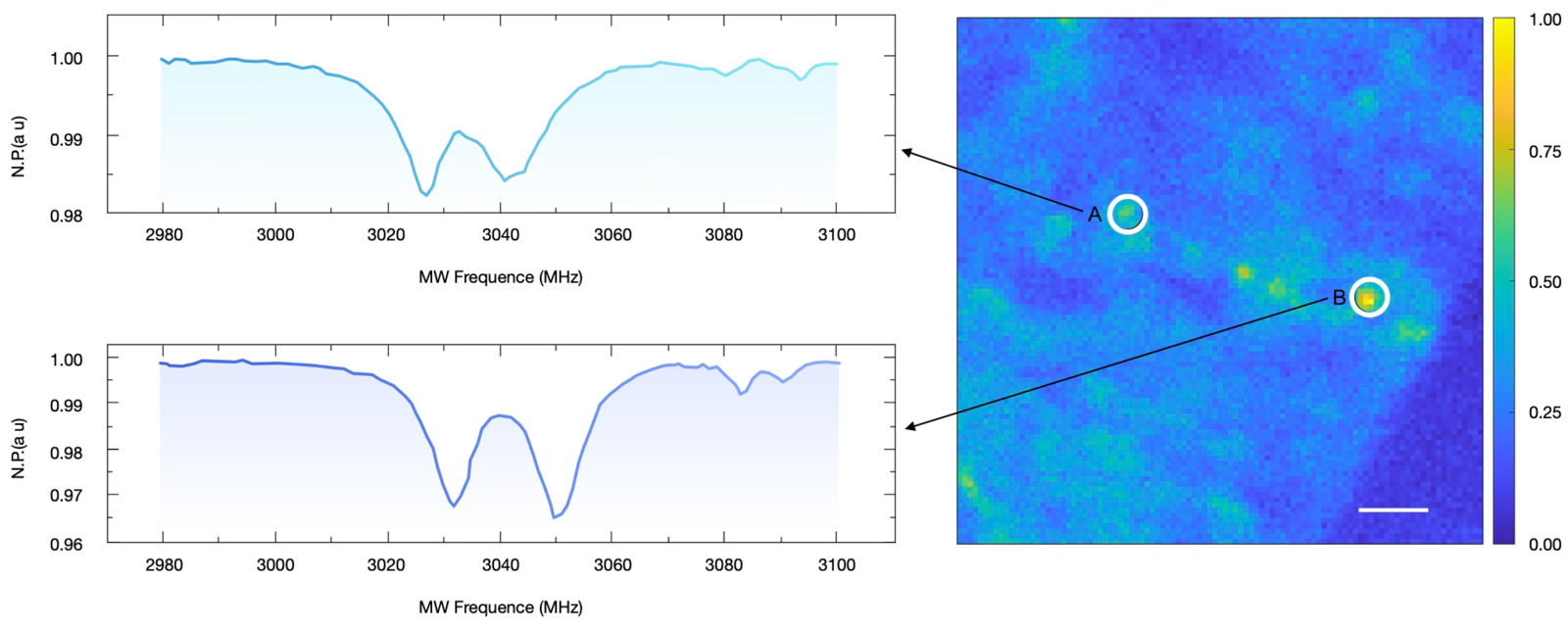
Fluorescence Collection Under Cryogenic High Pressure
(Long Working Distance)
NV center fluorescence analysis at 2 K, high-pressure (10 GPa) diamond anvil cell environment
Product model
MFLT36.VISNIR.APO
Fully Demagnetized, UHV Compatible, Broad Wavelength Apochromatic Range
Ultra-Long Working Distance
13.8 mm
In high-pressure optical experiments, diamond anvil cell setups require longer working distances
Specification
Explore Your Options
MFLT60.VIS.APO
MFLT36.VISNIR.APO
MFLT90.VIS
➨ Operating Environment
1 Operating Temperature
10 mK ~ 320 K
2 Maximum Operating Magnetic Field 1
18 Tesla
3 Operating Pressure
Vacuum ~ 1 standard atmosphere
➨ Optical Specifications
4 Numerical Aperture 2
0.6
0.36
0.9
5 Achromatic Range 3
T > 80 %
430 – 1050 nm
490 – 1500 nm
400 – 750 nm
6 Anti-Reflective 4
470 – 670 nm
470 – 1600 nm
450 – 630 nm
7 Imaging Distance
Focal Length ( f ) 5
Working Distance 6
Parfocal Distance
3.9 mm
6.0 mm
72.1 mm
6.7 mm
13.8 mm
72.1 mm

1.8 mm
0.2 mm
45 mm
8 Field of View 7
∅ 120 μm
∅ 220 μm
∅ 220 μm
9 Entrance Pupil Diameter 8
∅ 4.7 mm
∅ 4.8 mm
∅ 3.2 mm
10 Magnification 9
×51
×30
×111
➨ Basic Information
11 Dimensions
Diameter × Length
MFLT60.VIS.APO,
∅ 22.0 mm / 71.0 mm
MFLT36.VISNIR.APO,
∅ 21.0 mm / 63.0 mm
MFLT90.VIS,
∅ 22.0 mm / 49.5 mm



12 Weight
76.5 g
69.0 g
104.0 g
13 Materials
Titanium Alloy
Titanium Alloy
Copper Alloy
14 Thread
RMS ( WJ4 / 5 ”x 1 / 36″ )
15 Storage Conditions
Clean Room at Room Temperature, RH < 40%
- sMeasured Maximum Magnetic Field: The maximum field tested. Since the objective is made of fully demagnetized materials, it can theoretically operate in even stronger magnetic fields.
- Numerical Aperture (N.A.): N.A. = n · sin(θ/2), where n is the refractive index of the medium between the objective and the sample, and θ is the aperture angle, defined as the maximum cone of light the system can accept. This parameter determines the resolution of microscopic imaging, with the minimum resolvable distance between two points given by d = 0.61 λ / N.A. (λ is the wavelength of the light source).
- Achromatic Range: Achromatic Range – the focal point of light at different wavelengths may shift (|df|), but as long as the shift is within the depth of focus (Δ = λ / 2 × N.A.²), imaging quality is unaffected. The wavelength range satisfying |df| < Δ is called the apochromatic range; the range corresponding to dfλ1–λ2 < |Δ| (where λ1 and λ2 are the ends of the working wavelength band) is called the achromatic range.
- Anti-Reflective Coating (A.R.): The percentage of transmitted light (T) at specific wavelengths after passing through the objective, relative to the incident light.
- Focal Length (f): A key optical parameter, defined as the distance from the optical center to the focal point. It is widely used in calculating various optical specifications.– Optical Center (Objective Center): The point through which light passes without deviation, serving as the coordinate origin of the microscope optical system.-Focal Point: The point where parallel light rays converge after passing through the objective.
- Working Distance (W.D.): The vertical distance from the mechanical front end of the objective (the lowest point of the metal housing protecting the front lens) to the sample surface when the sample is in focus.
- Field of View (FOV): The diameter of the area on the objective’s focal plane with diffraction-limited imaging quality.
- Entrance Pupil Diameter: The maximum diameter of parallel light that can pass unobstructed through the objective.
- Magnification: The objective itself produces parallel light, which cannot form an image directly. In practice, it must be used with a tube lens to form an image. The stated magnification refers to using a 200 mm focal length tube lens.
Product Data
Down.List
Product Declarations
2D / 3D file
Huygens Manual
Consultation Purchase
Contact us